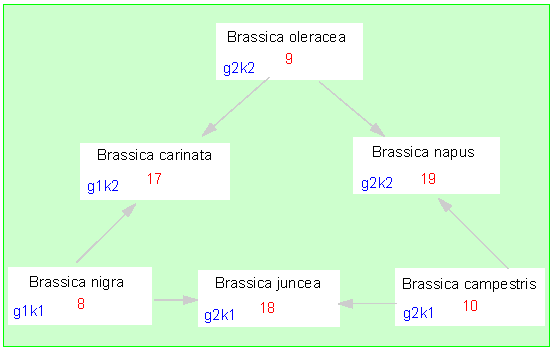
Development of three cultivated Brassica-species by species hybridization and allopolyploidization (haploid chromosome sets in red) (N. U, 1935; O. WINGE; 1917). The model could be confirmed by molecular analyses. Tested were the composition of a protein (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase) (M. B. ROBINS and J. G. VAUGHAM, 1983) and the structure of the respective gene (J. D. PALMER et al, 1983). Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase consists of a large (g) and a small (k) subunit. The different genotypes are marked 1 and 2 (blue). Brassica carinata, for example, contains the gene for the large subunit from Brassica nigra and that of the small subunit from Brassica oleracea. Additionally, genetic engineering was used. The scheme was supplemented by further species (more in: K. GLIMELIUS et al., 1991)