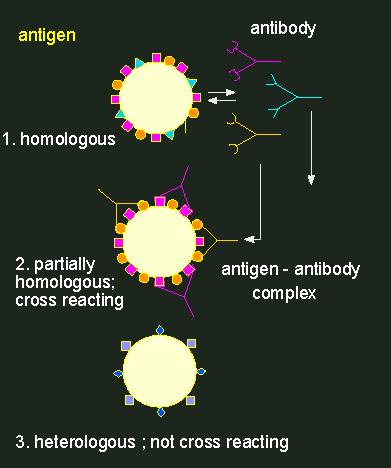
Antibodies (depicted as Y-shaped structures) form a heterogeneous population of molecules with different specificities. A cross-reaction of an antibody population (an anti-serum) with a foreign antigen (in the middle) occurs only, if the homologous and the foreign antigen are at least partially equipped with the same determinants. Every antibody has two identical binding sites for antigen determinants.