NAD: oxidized and reduced forms
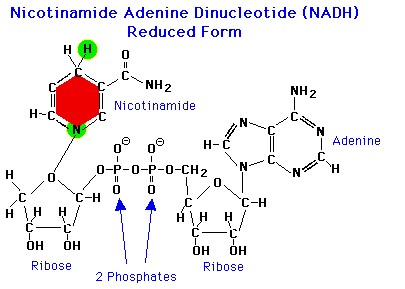
As NAD is reduced, one electron is added at the Nitrogen atom (removing the + charge), and one (electron + proton = H atom) is added at the upper position of the nicotinamide ring.
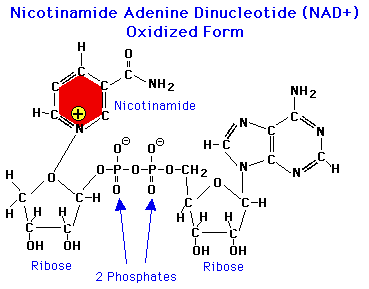
NAD in the oxidized form contains the elements of ADP, with an additional ribose molecule and a nicotinamide ring. The latter is the critical element in redox reactions. When a pair of H atoms (2 protons + 2 electrons) are removed from organic substrates in an oxidation reaction, NAD+ accepts 2 electrons and 1 proton; the remaining proton is released as free H+ ion.

