| TROPISM |
STIMULUS |
BIOLOGICAL CHANGE |
RESPONSE |
| Positive phototropism |
light |
Cell elongation is stimulated on the shaded side of a stem but inhibited on the lighted side. |
Growing shoot bends towards the light. |
| Positive gravitropism |
gravity |
Cell elongation is inhibited on the lower portion of the root but stimulated on the upper portion. |
Growing root bends downwards towards the centre of the gravity. |
| Positive thigmotropism |
touch or pressure |
Cell elongation is inhibited on the stem side touching an object but stimulated on the non-touching side |
Growing shoot coils around the object. For example, in some climbing vines. |
| Negative thigmotropism |
touch or pressure |
Cell elongation is stimulated on the stem side touching an object but inhibited on the non-touching side. |
Shoot grows away from an obstacle. |
| Positive hydrotropism |
water availability |
Root tips closest to a source of water and soluble minerals simply grow faster than those further away. (Hormones not involved here.) | Growth of the root towards a water source. |
| ENVIRONMENT (and plant type) |
ADAPTATIONS |
| HOT AND DRY (xerophytes) |
- Stomata closed during heat of day
- Reduced or absent leaves (cacti)
- Leaves aligned away from direct sunlight
- Stoma almost all on lower leaf surface
- Stoma protected in pits or surrounded by hairs
|
| HOT AND HUMID (tropical) |
Guttation (drops of water released from leaf surface) removes excess water which enters plant due to root pressure. |
| VERY COLD WINTERS - temps below 0oC |
- Deciduous - plants lose leaves and reduce metabolism to ensure survival.
- Leaf oils - act as 'anti freeze' to protect, as in conifers.
- Vernalization ensures that reproduction occurs during warm weather.
|
| FRESH WATER (aquatic plants = hydrophytes) |
- Large vacuoles collect and expel excess water.
- Large air spaces in leaves allow leaves to float on or near surface and obtain light.
- Reduced stomata - gas exchange is by diffusion in/out of water.
|
| MARINE (algae) seaweed |
- Non chlorophyll pigments (so they are not always green) since penetration of light is different under water.
- Flotation bladders, full of air, hold fronds near surface where light and gas levels are highest.
- Holdfasts anchor plants in presence of strong tides and currents (not true roots, since water is plentiful and minerals diffuse from environment).
|
| HIGH SOIL [SALT] (halophytes) eg mangroves |
- Salt excreted through leaves
- Very thick leaf epidermis protects from salt.
|
| LOW SOIL [MINERAL] (carnivorous plants) |
- Special structures attract and trap insects.
- Enzymes digest the insects, releasing minerals to diffuse into plant.
|




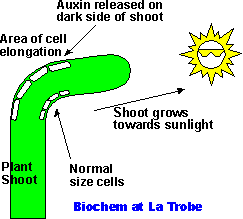 Here is a classic diagram of a shoot bending towards the light. Note how auxin released only on the dark side of the shoot is able to cause cell elongation on that side. It is the uneven cell growth which causes the shoot to bend - towards the light in this case to optimise the exposure to the light for photosynthesis.
Here is a classic diagram of a shoot bending towards the light. Note how auxin released only on the dark side of the shoot is able to cause cell elongation on that side. It is the uneven cell growth which causes the shoot to bend - towards the light in this case to optimise the exposure to the light for photosynthesis.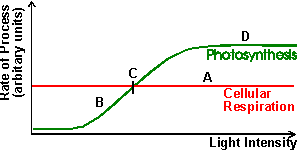 Graph of rates of cellular respiration and photosynthesis at varying light intensities. Note the following:
Graph of rates of cellular respiration and photosynthesis at varying light intensities. Note the following: