![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
You can click to go straight to any one of the following topics:

| NAME | SIZE AND STRUCTURE | LIVING CONDITIONS | EXAMPLES | PREVENTION | CURE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
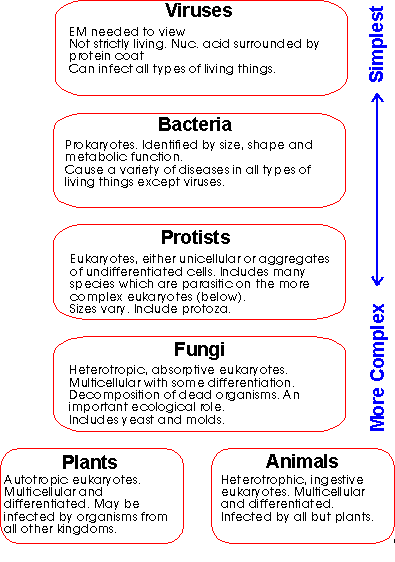
| VIRUSES | 20-100 x 10-9M Electron microscope to view. Protein coat with DNA or RNA inside. Maybe membrane outer layer. | Unable to live outside other cells.May infect prokaryotes and/or eukaryotes.Replicates inside host cell by coding (with viral nucleic acid) for new viral synthesis there. | Bacteriophages, Plant mosaic viruses, HIV, Herpes, Influenza, Hepatitis | Good personal hygiene. Some immunisation(eg 'flu, polio) | NOT antibiotics. Immune system fights viruses. Recently, some antiviral drugs developed. |
| BACTERIA | 0.1-1.0 x 10-6M Light microscope (Stains aid identification) Prokaryotes - Revise structure! (Kingdom Monera) | Ubiquitous. In almost all environmental niches. Most are non pathogens.Pathogenic bacteria:Cause disease in eukaryotes. Classified by shape (spheres, rods, spirals). Classified by chemistry (eg Gram +/-) Classified by structures (cilia, flagella) Some produce destructive toxins. | Streptococcus, Salmonella, Staphylococcus, Escherischia coli (E. coli) Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Clostridium tetani | Good personal hygiene. Immunisation (eg TB), Public sanitation, Surgical aseptic techniques. | Various antibiotics.(1928 Fleming discovered penicillin, 1938 Florey developed it for human use.) Anti-toxins (eg tetanus) |
| FUNGI | Most are microscopic (L.M.) (eg yeast) Some are macroscopic | Yeasts - Unicellular, divide by binary fission or budding. Can exist as spores.Moulds - Filamentous mat of thread-like hyphae produces a mycelium. Fruiting bodies produce spores.(Some pathogenic fungi can exist as either of the above forms, depending on the environment.) | Candida (-> thrush) Trichophyton (-> tinea) Aspergillus (-> pneumonia or asthma) | Good personal hygiene. | Various anti-fungal drugs. |
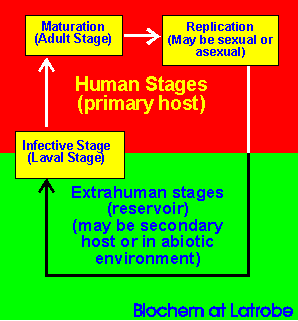
| PARASITES | Some microscopic. (eg Plasmodium vivax -> malaria, Entamoeba histolytica -> dysentery)Some macroscopic (eg fleas, ticks, tapeworm, hydatids) ALL ARE EUKARYOTES | Either ectoparasites (outer surfaces of host) or endoparasites (inside host's body). Many have complex life cycles which include a period away from humans and a time in or on humans. Many have specialised structures for attachment to humans either to prevent dislodgment or obtain nutrients or both. VECTOR = living transmitter of disease (eg mosquito -> malaria) RESERVOIR = source of parasite in abiotic environment (eg contaminated soil or water). | Malaria, Dysentery, Liver fluke, Intestinal worms, Schistoma, Fleas, Ticks, Lice | Good personal hygiene.Public sanitation.Break life-cycle.Cook meat before eating. | Some insecticides. Some drugs.Surgery to remove cysts.Topical insecticides. |