|
|
|
small molecules: |
|
in spacefilling presentation |
the electron cloud is shown by dots |
|
Carbohydrate chains are called aliphatic hydrocarbons. Molecules that share the same formula but have different structures are structural isomers. Carbohydrate chains containing multiple bonds are also termed unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alcohols are aliphatic carbon compounds that carry on or more hydroxyl-groups directly linked to a carbon atom. The dehydration of primary alcohols leads to aldehydes that of secondary alcohols to ketones. The oxidation of an aldehyde group leads to an organic acid. Esters are produced by a condensation reaction of an alcohol and an acid.
Carbon with its four outer-shell electrons can form four strong covalent bonds. The simplest carbohydrate would thus be
|
|
|
|
|
methane |
|
Furthermore, carbon has the ability to form large chains. Carbohydrate chains are also called aliphatic hydrocarbons and have the collective formula CnHn+2. The simplest examples are:
H H
| |
H - C - C - H
| |
H H
|
H H H
| | |
H - C - C - C - H
| | |
H H H
|
H H H H
| | | |
H - C - C - C - C - H
| | | |
H H H H
|
|
ethane |
propane |
butane |
Branchings may occur, for example in
CH3 | CH3 - C - CH3 | H |
| isobutane |
The more C-atoms a molecule has, the more variations are possible. Such variations are called structural isomers. Carbohydrate chains containing multiple bonds (double bonds, triple bonds) are called unsaturated hydrocarbons (in contrast to the saturated ones just talked about).
Aliphatic hydrocarbons with double bonds are:
H H
\ /
C = C
/ \
H H
|
H H
\ /
H C = C
\ / \
C = C H
/ \
H H
|
H H
\ /
H C = C
\ / \
C = C H
/ \
H CH3
|
|
ethylene |
butadiene |
isoprene |
The latter compound has, apart from the double bond, a branching. This substance is the source product of carotenoid biosynthesis and of numerous secondary plant components.
A carbohydrate with a triple bond is
Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons may also occur as rings. The best-known compounds are:
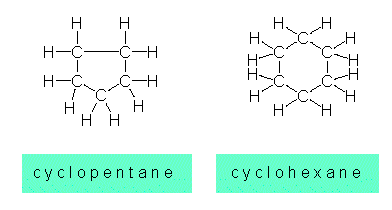
The C-atoms are not in one plane, but exist in two different conformations (seat (chair) and boat):
|
cyclohexane |
|
|
seat conformation |
boat conformation |
|
|
|
Such conformations are especially important for the understanding of sugar chemistry.
|
gallery: structure and data of a few aliphatic hydrocarbons |
|
|